Limited Time Offer 👉 Get 58% off Divi AI with the Divi Pro.
What Is a Search Engine: How They Work, Why They Matter and What’s Next
In today’s digital world, the term Search Engine is synonymous with access to information. Whether you’re looking for the best Italian restaurant nearby, scientific research papers, or troubleshooting your laptop, you likely turn to a search engine first. But how do search engines work? What happens behind the scenes when you type a query?
Let’s dive deep into the world of search engines, explore their history, technology, challenges, and future.
What Is a Search Engine?

A search engine is a software system designed to carry out web searches. It systematically searches the Internet or a database for information based on user queries and presents the results, typically ranked by relevance.
The most well-known example is Google, but there are many others including Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo and Yandex.
At a high level, a search engine performs three key functions:
- Crawling – Scouring the Internet for content.
- Indexing – Organizing and storing content.
- Ranking and Retrieving – Fetching and presenting the most relevant results to users.
History of Search Engines
The journey of search engines began in the early 1990s:
- 1990: Archie was created — the first tool to index FTP archives, allowing people to find specific files.
- 1994: WebCrawler introduced full-text search of webpages.
- 1995-1997: Launch of Yahoo!, AltaVista, Ask Jeeves, and Excite.
- 1998: Google was founded by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, revolutionizing search with a focus on relevancy using their PageRank algorithm.
- 2000s onward: Innovations continued — with Google’s dominance growing, Bing by Microsoft gaining ground, and privacy-focused engines like DuckDuckGo emerging.
How Search Engines Work?
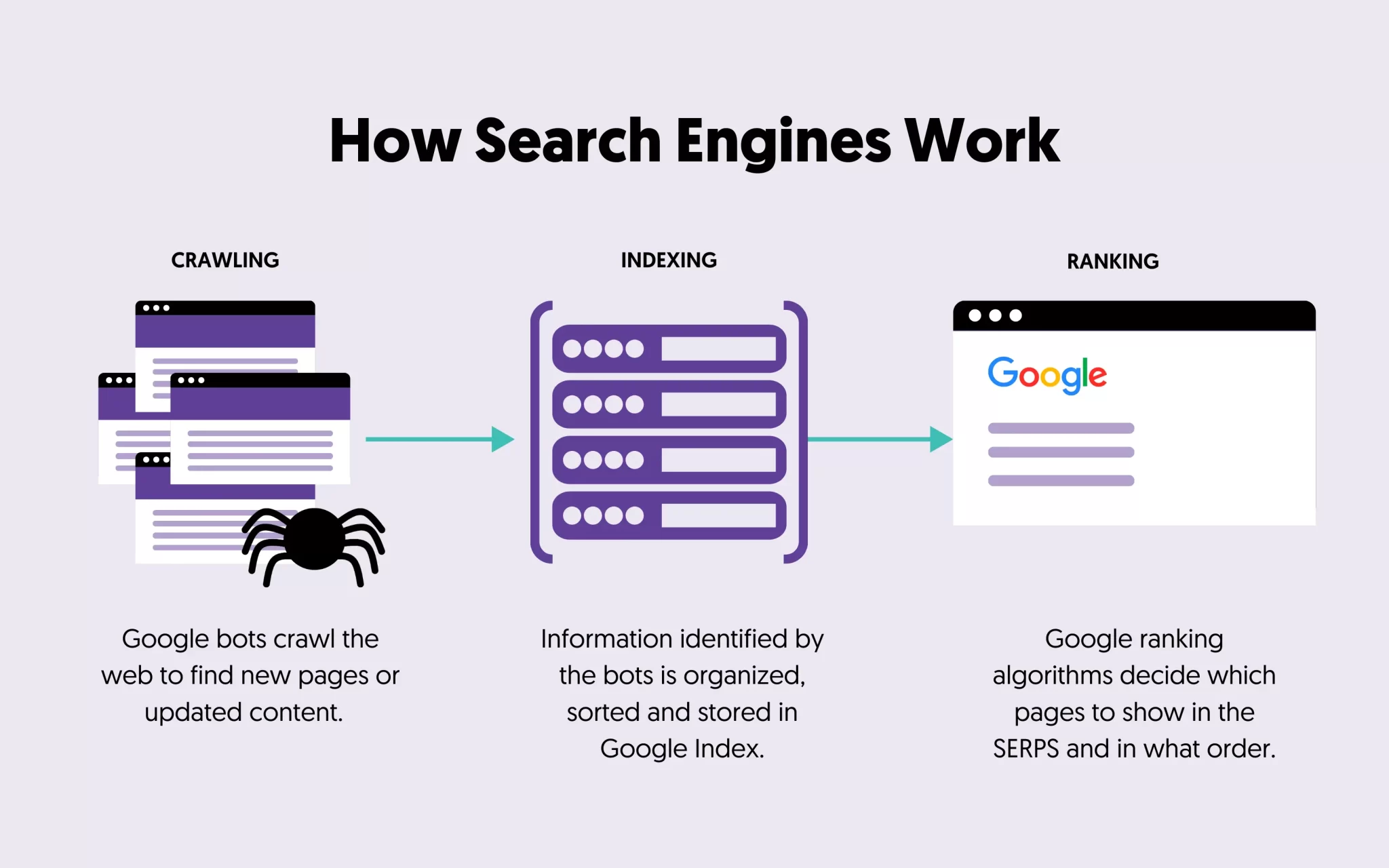
- Crawling:
- Crawling is the discovery process. Search engines send out bots (also called spiders or crawlers) to find new and updated content. This could be a webpage, an image, a video, a PDF, etc.
- Crawlers follow links from known pages to new ones.
- They scan a site’s structure, looking at text, keywords, and metadata.
- Tools like robots.txt files control what crawlers are allowed to access.
- Crawling is the discovery process. Search engines send out bots (also called spiders or crawlers) to find new and updated content. This could be a webpage, an image, a video, a PDF, etc.
- Indexing:
- Once content is discovered, it is indexed — stored and organized in a vast database.
- The index is a massive library of all the information search engines have found and deem good enough to serve to users.
- Content is analyzed for keywords, freshness, website authority, page structure (headings, titles, meta tags), and more.
- Once content is discovered, it is indexed — stored and organized in a vast database.
- Ranking and Retrieval:
- When a user enters a query:
- The search engine sifts through its index, not the live web.
- It uses complex algorithms to rank pages based on relevance, authority, usability, and context.
- Results are displayed in an ordered list on a Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
- Factors that influence rankings include:
- Keyword relevance.
- Quality and quantity of backlinks.
- Page load speed.
- Mobile-friendliness.
- Domain authority.
- User engagement metrics (like bounce rate, dwell time).
- When a user enters a query:
Components of a Search Engine:
A search engine is not a single tool but a complex system composed of multiple interconnected components, each responsible for a specific function. These components work together to find, store, analyze, and serve relevant information in response to a user’s query.
The major components are:
- Web Crawler (Spider or Bot):
- Purpose: Discover and collect content from across the Internet.
- What it does:
- A web crawler systematically browses the web to find new or updated pages. It starts from a set of known pages and follows hyperlinks to discover more content.
- Key responsibilities:
- Fetch HTML pages and other assets (images, videos, PDFs).
- Read and respect the
robots.txtfile to understand which parts of a website are allowed or disallowed for crawling. - Update previously crawled pages if they have changed.
- Popular examples:
- Googlebot (Google)
- Bingbot (Bing)
- Baidu Spider (Baidu)
- Challenges:
- Managing crawling frequency (not to overload websites).
- Avoiding crawling duplicate content.
- Prioritizing important and frequently updated content.
- Indexer:
- Purpose: Organize and store the crawled data for fast retrieval.
- What it does:
- The indexer processes and parses the crawled content to extract useful information and create an organized index (similar to an index in a book).
- Key responsibilities:
- Extract keywords, metadata, links, headings, etc.
- Analyze page structure (title tags, H1/H2 tags, paragraph texts).
- Create inverted indexes (mapping keywords to pages).
- Store ranking signals like freshness, page quality, and user engagement.
- Challenges:
- Handling the massive volume of data (the web has billions of pages).
- Efficiently updating the index when pages change or are deleted.
- Storing different types of content (text, images, video, audio).
- Database:
- Purpose: Store indexed data for quick access during search queries.
- What it does:
- A search engine’s database is a giant repository that stores the structured information collected and processed by the indexer.
- Key responsibilities:
- Provide fast and scalable data storage.
- Ensure data integrity and consistency.
- Enable quick lookup for search requests.
- Challenges:
- Handling huge amounts of structured and unstructured data.
- Replicating data across different data centers worldwide.
- Maintaining high availability and quick access speeds.
- Query Processor:
- Purpose: Interpret user queries and fetch matching results.
- What it does:
- When a user enters a search term, the query processor interprets it and retrieves the most relevant documents from the database.
- Key responsibilities:
- Parse and understand the query.
- Expand or refine queries (e.g., handling synonyms, spelling corrections).
- Apply ranking algorithms to sort results.
- Personalize results based on user location, search history, or preferences.
- Challenges:
- Understanding user intent (informational, transactional, navigational).
- Handling ambiguous or complex queries.
- Delivering results instantly (in milliseconds).
- Ranking Engine (Algorithm):
- Purpose: Decide the order of search results based on relevance and importance.
- What it does:
- The ranking engine scores each result based on hundreds (sometimes thousands) of ranking factors and then orders them.
- Key responsibilities:
- Evaluate content relevance (how closely the page matches the query).
- Assess page quality (trustworthiness, authority, backlink profile).
- Analyze user engagement signals (click-through rates, bounce rates).
- Incorporate real-time signals (trending topics, breaking news).
- Adjust rankings for personalization and localization.
- Key ranking factors:
- Keywords in title and content
- Page authority and backlinks
- Page load speed
- Mobile-friendliness
- Content freshness
- Secure websites (HTTPS)
- Challenges:
- Combating SEO manipulation (keyword stuffing, link farming).
- Balancing different types of search intents.
- Providing fair and unbiased results.
- User Interface (Search Interface):
- Purpose: Allow users to input queries and view results.
- What it does:
- The search interface is what users see and interact with — typically a search bar, search suggestions, and results page.
- Key responsibilities:
- Provide a clean and intuitive interface.
- Offer features like auto-suggestions, filters, and advanced search.
- Display results with snippets (title, URL, description).
- Handle voice search and visual search capabilities.
- Challenges:
- Designing for usability and accessibility.
- Supporting multiple languages.
- Delivering search results quickly and visually appealingly.
- Feedback System:
- Purpose: Learn from user interactions to improve search results.
- What it does:
- Search engines monitor how users interact with search results to refine future rankings.
- Key responsibilities:
- Track clicks, time spent on pages, bounce rates.
- Analyze which results satisfy users and which don’t.
- Use machine learning to adjust algorithms based on feedback.
- Challenges:
- Ensuring data privacy.
- Distinguishing genuine user satisfaction from manipulated behaviors.
Importance of Search Engines:
- Accessibility of Information:
- Search engines make information easily and quickly accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
- Democratization of Knowledge:
Before engines, accessing information often meant trips to libraries, archives, or experts. Now, a search query can retrieve millions of results in seconds, empowering people worldwide regardless of their location or background. - Real-Time Updates:
Search engines index fresh content constantly. This means users get up-to-date information on breaking news, scientific developments, and global events as they happen.
- Democratization of Knowledge:
- Search engines make information easily and quickly accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
- Critical for Education and Research:
- Search engines are indispensable tools for students, educators, and researchers.
- Academic Research:
Scholarly articles, journals, theses, and educational resources are accessible instantly, enabling deeper learning. - E-Learning and Online Courses:
Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy are more discoverable through engines, promoting lifelong learning. - Fact-Checking and Verification:
In an age of misinformation, engines help users quickly cross-reference information and verify facts.
- Academic Research:
- Search engines are indispensable tools for students, educators, and researchers.
- Driving Business and E-commerce:
- For businesses, visibility on search engines is critical to success.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
Companies invest in SEO to ensure their websites rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs), which can significantly increase traffic and sales. - Consumer Decision-Making:
Most customers research products online before purchasing. Positive reviews, comparisons, and testimonials found through searches influence buying decisions. - Local Search and Small Business Growth:
Search engines help local businesses connect with nearby customers through local SEO strategies, Google Maps listings, and “near me” searches.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
- For businesses, visibility on search engines is critical to success.
- Essential for Digital Marketing:
- Search engines are central to all forms of digital marketing strategies.
- Paid Search (PPC Advertising):
Businesses pay for their ads to appear at the top of search results (e.g., Google Ads). These targeted ads offer high conversion rates. - Content Marketing:
Brands create blogs, videos, and infographics optimized for engines to attract, educate, and convert audiences. - Brand Visibility and Trust:
Ranking high on engines boosts a brand’s credibility. Users often perceive top-ranking brands as more trustworthy and authoritative.
- Paid Search (PPC Advertising):
- Search engines are central to all forms of digital marketing strategies.
- Empowering Personal Productivity:
- Search engines enhance individual efficiency in everyday tasks.
- Problem-Solving:
From finding recipes to troubleshooting tech issues, engines help users find quick solutions. - Learning New Skills:
DIY tutorials, coding classes, language learning — all start with a search query. - Travel Planning:
Searching for flights, hotels, attractions, and reviews simplifies organizing trips.
- Problem-Solving:
- Search engines enhance individual efficiency in everyday tasks.
- Impact on Society and Culture:
- Search engines play a significant role in shaping public opinion and culture.
- Social Awareness:
People discover social causes, global movements, and campaigns (like climate change activism or human rights efforts) through searches. - Political Influence:
Engines impact political opinions, especially during elections when people search for candidates, policies, and news. - Cultural Trends:
Trends, memes, and viral phenomena are often born or spread via search engine discovery.
- Social Awareness:
- Search engines play a significant role in shaping public opinion and culture.
- Enabling Technological Advancement:
- Search engines are not just tools; they are drivers of innovation.
- AI and Machine Learning:
Engines like Google use artificial intelligence (e.g., RankBrain) to better understand queries, learn from behavior, and improve over time. - Voice and Visual Search:
Technologies such as Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa rely on sophisticated search algorithms to respond to voice commands and visual cues. - Big Data Analytics:
It analyze vast amounts of user data to improve user experiences and fuel technological developments in predictive analytics, recommendation systems, and personalization.
- AI and Machine Learning:
- Search engines are not just tools; they are drivers of innovation.
- Privacy, Ethics, and Regulation:
- While search engines provide enormous benefits, they also raise important ethical considerations.
- Data Privacy:
Users’ search data can be tracked to personalize ads or experiences, but this also raises concerns about surveillance and misuse of data. - Algorithmic Bias:
How it rank and display information can influence public perception. Ensuring neutrality and fairness in algorithms is a growing concern. - Regulatory Environment:
Governments are increasingly imposing regulations (e.g., GDPR in Europe) to protect user privacy and maintain fair competition in the search engine market.
- Data Privacy:
- While search engines provide enormous benefits, they also raise important ethical considerations.
Major Players in the Search Engine Market
| Search Engine | Key Strengths | Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Speed, relevance, innovation | Global | |
| Bing | Integration with Microsoft products | U.S., enterprise |
| Yahoo! | Email and news integration | U.S., Japan |
| Yandex | Search leader in Russia | Russia |
| DuckDuckGo | Privacy-focused | U.S., Europe |
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO is the art and science of making web pages rank higher in search engines.
Key aspects of SEO include:
- On-page SEO: Optimizing content, meta tags, and internal links.
- Off-page SEO: Building backlinks and external signals.
- Technical SEO: Improving site architecture, speed, mobile-friendliness, and security.
- Content Strategy: Creating valuable, targeted content that answers user queries.
Without SEO, even the best content can remain hidden.
Challenges Faced by Search Engines
- Spam and Manipulation: Black-hat SEO techniques try to trick algorithms.
- Fake News and Misinformation: Ensuring the credibility of indexed content.
- Privacy Concerns: Collecting user data raises ethical and regulatory issues.
- Monopolization: Few companies dominate the market, leading to debates about fair competition.
- Multimedia Search: Improving search for non-text content like images and videos.
- Voice and Conversational Search: Adapting to new ways people search (e.g., Siri, Alexa).
Future of Search Engines
The future of search is bright and fast-evolving:
- AI and Machine Learning: Google’s RankBrain and other AI models are changing how results are interpreted.
- Voice Search: By 2025, more than 50% of all searches may be voice-based.
- Visual Search: Tools like Google Lens allow users to search using images.
- Personalized Search: Engines will continue tailoring results based on individual behavior and preferences.
- Decentralized Search: Blockchain-based search engines could give users more control over their data.
Conclusion
Search engines are the gateway to the world’s knowledge. They have evolved tremendously from simple keyword matchers to complex AI-driven systems capable of understanding user intent. As technology advances, search engines will become even more integral to daily life — smarter, faster, and more personalized.
Understanding how they work not only helps businesses optimize their presence but also helps users better navigate the infinite world of information.
In a world overflowing with content, search engines are our most trusted guides — and their evolution is only just beginning.